Fix the "Sitemap Could Not Be Read" Error
Stop struggling with Google Search Console errors. Get your sitemap indexed properly and watch your organic traffic grow.
Try IndexJump Free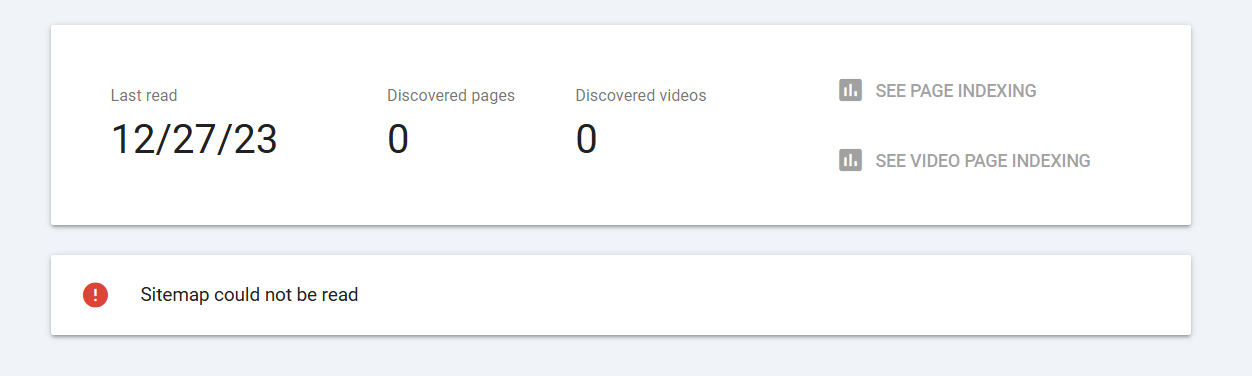
Stop struggling with Google Search Console errors. Get your sitemap indexed properly and watch your organic traffic grow.
Try IndexJump Free
Explore our expertise in solving sitemap and indexing issues
Website owners and developers often rely on sitemaps to improve search engine optimization (SEO) and ensure that their site's content is properly indexed. However, encountering issues such as the "sitemap could not be read" error can disrupt this process and cause concern. This comprehensive guide explores the common reasons behind this problem, how to diagnose it, and practical solutions to resolve the issue effectively.
A sitemap is a file that lists all the important pages of a website, providing search engines with a roadmap of your content. Sitemaps are typically written in XML format and serve as a guide for search engines to crawl and index your website efficiently. Accurate and up-to-date sitemaps help improve your site's visibility, enhance ranking, and ensure fresh content is discovered promptly.
The message that a sitemap cannot be read can stem from various issues. Recognizing the underlying cause is crucial to applying the correct fix. Below are some typical reasons:
If the URL provided to search engines or tools is misspelled or points to an incorrect location, the sitemap cannot be accessed or read. Verify the exact URL and ensure it matches your hosted sitemap location.
Malformed XML files, such as missing tags or invalid characters, can prevent search engines from parsing the sitemap correctly. Validating your sitemap with XML validators helps identify and fix syntax errors.
If your server is down, experiencing high traffic, or has misconfigured permissions, the sitemap file may not be accessible. Check server status, ensure proper permissions are set, and verify that the site is reachable.
Rules specified in your robots.txt file may disallow access to the sitemap URL, blocking search engines from reading it. Review your robots.txt to ensure the sitemap URL is not disallowed.
The server should serve XML sitemaps with the correct Content-Type header (application/xml or text/xml). Incorrect headers can cause reading errors.
Large sitemaps or network connectivity issues might interfere with the reading process. Ensure your sitemap does not exceed recommended size limits and check network stability.
Diagnosing the root cause involves systematic checks:
Ensure that the URL submitted to search engines or used in tools exactly matches your hosted sitemap location. Update or correct the URL if needed.
Use online XML validators to identify errors in your sitemap. Correct issues such as unclosed tags, invalid characters, or misplaced syntax to make it compliant.
Check server configurations, permissions, and hosting status. Set the correct permissions for the sitemap file to be publicly accessible. Ensure the server is running smoothly.
Modify your robots.txt file to ensure that the sitemap URL is not disallowed. For example, add a line like Sitemap: https://www.site.com/sitemap.xml if not already present.
Configure your server to serve your sitemap with the Content-Type header set to application/xml or text/xml. This ensures proper recognition and reading.
If your sitemap is very large, split it into smaller, linked sitemap files following sitemap protocol guidelines. This can improve readability and indexing efficiency.
Staying proactive in maintaining your sitemap helps prevent read errors. Use tools like Google Search Console or Bing Webmaster Tools to monitor your sitemap’s status. These platforms can alert you to issues and provide recommendations for fixes.
In conclusion, resolving the "sitemap could not be read" message involves a combination of verifying URL correctness, ensuring proper formatting, maintaining server accessibility, and adhering to best practices. By systematically diagnosing and addressing common causes, website owners can ensure their sitemaps serve their purpose effectively, leading to better search engine visibility and overall site health.
Google Search Console (GSC) is an essential tool for website owners and SEO professionals, providing insights into how Google crawls and indexes your website. One common issue faced by users is the error message: "Google Search Console sitemap could not be read." This article offers a comprehensive overview of what this error means, potential causes, and practical solutions to address it effectively.
A sitemap is a file that lists all the important pages of your website, helping search engines like Google to crawl and index your content more efficiently. Sitemaps support various formats, most commonly XML, and include details such as page priority and last modification date.
Implementing a sitemap enhances the visibility of your website in search results, ensures new or updated pages are discovered swiftly, and improves overall SEO performance. Therefore, a functional sitemap is vital for optimal indexing.
When Google Search Console reports that your sitemap could not be read, it indicates a problem preventing Google from accessing or parsing the sitemap file. This can hinder Google’s ability to crawl your site properly, potentially impacting search visibility.
The error typically appears under the Sitemaps section in GSC and is accompanied by details pointing to specific issues with the sitemap URL or content.
If the URL submitted in GSC is incorrect, misspelled, or points to a non-existent location, Google cannot locate or read the sitemap. Ensure the URL is correct and accessible.
Server-side issues such as server downtime, misconfigured permissions, or firewall restrictions can prevent Google from fetching the sitemap file. Confirm that the server hosting the sitemap is operational and accessible publicly.
An improperly formatted sitemap—such as malformed XML—can cause read errors. Use validators or tools to verify the correctness of the sitemap file.
The robots.txt file may block Google from crawling the sitemap URL, resulting in read errors. Check for disallow rules that might be blocking access.
Very large sitemaps exceeding size limits or containing complex structures can sometimes cause issues. Consider breaking large sitemaps into smaller, manageable files.
Temporary network issues between Google’s crawlers and your website can lead to difficulties reading sitemaps. These are usually transient and resolve on their own.
Check that the URL submitted in GSC matches the actual location and format of your sitemap. Access the URL directly in a browser to ensure it loads without errors.
Use online XML validators or sitemap-specific tools to check for syntax errors or formatting issues. Correct any problems identified.
Ensure the server hosting your sitemap is running correctly and that there are no restrictions blocking Google’s access, such as IP blocking or firewall rules.
Open your robots.txt file and confirm that the sitemap URL is not disallowed. To verify, you can temporarily remove any disallow rules for the sitemap URL and test again.
If your sitemap exceeds 50,000 URLs or surpasses 50MB, consider splitting it into smaller sitemaps linked via a sitemap index file. This ensures compliance with Google's guidelines and reduces read errors.
After fixing issues, remove the existing sitemap from GSC and resubmit it. Monitor the status to see if the error persists.
Use tools like Pingdom or GTmetrix to analyze your website’s server response times and availability. Resolve any downtime or connectivity problems.
While addressing the "sitemap could not be read" error, consider the broader context of your website’s SEO health. Ensure your robots.txt file is configured correctly, verify your website’s overall crawl budget, and optimize server performance.
Regular audits and proactive management of your sitemaps help maintain optimal visibility in search engine results and prevent future errors.
Besides Google Search Console, several tools can analyze your sitemap and server setup:
Combining these tools with thorough manual checks ensures a comprehensive approach to resolving the sitemap read error.
Addressing the "Google Search Console sitemap could not be read" error requires a methodical approach involving verification, validation, and correction of your sitemap and server configurations. By following best practices and leveraging appropriate tools, you can restore seamless communication between your website and Google, supporting better indexing and improved search visibility.
Sitemaps are essential files that provide search engines with information about the pages, videos, and other content on your website. They help search engines crawl and index your website more efficiently, ensuring that your content appears in search results. A sitemap is typically an XML file that adheres to specific standards to communicate effectively with search engines like Google.
When implementing a sitemap, website owners may encounter issues, such as receiving messages that the "Google sitemap could not be read." This problem can prevent Google from properly crawling your site and can negatively affect your search visibility.
The error message "Google sitemap could not be read" indicates that Google Search Console is unable to access or parse your sitemap file successfully. This problem can stem from various causes, including server issues, formatting errors, or permission problems.
Understanding the root causes of this issue is vital to resolving it efficiently. The primary concern is that Google cannot retrieve or interpret your sitemap, leading to incomplete or failed indexing of your website’s pages.
If the sitemap URL provided in Google Search Console is incorrect or misspelled, Google won't be able to locate your sitemap. Double-check that the URL is accurate and points directly to the sitemap file.
Accessibility issues, such as server downtime, misconfigured permissions, or firewall rules, can prevent Google from fetching your sitemap. Ensure that the Sitemap is accessible publicly without restrictions.
XML files need to adhere to proper syntax and standards. Any formatting errors, such as unclosed tags or invalid characters, can cause Google to fail reading the sitemap.
Sitemaps exceeding the recommended size (50MB uncompressed) or containing more than 50,000 URLs can cause issues. You may need to split large sitemaps into smaller, manageable files.
HTTP errors like 404 (Not Found), 403 (Forbidden), or 500 (Server Error) indicate issues with server response, making the sitemap inaccessible.
Check that the URL submitted in Google Search Console correctly points to your sitemap location. Test the URL by opening it in a browser to ensure it loads without errors.
Google Search Console provides tools to test your sitemap. Use the "Test Sitemap" feature to identify specific errors or issues with your sitemap file.
Use XML validators or sitemap validation tools to ensure that your sitemap conforms to standards. Correct any syntax errors and ensure all URLs are properly formatted.
Make sure your server is up and running, with no restrictions that block Googlebot. Check that the sitemap file is publicly accessible and not restricted by robots.txt or IP blocks.
If your sitemap size is too large, divide it into multiple smaller sitemaps and create a sitemap index to manage them collectively.
Use tools like cURL or online HTTP status checkers to verify server responses. Address any errors encountered during these checks.
For further assistance, consider the following resources:
If you are managing a website and using Google Search Console, encountering the message "Sitemap could not be read" can be frustrating. This notification indicates that Google is unable to access or interpret your sitemap properly. Understanding the causes and solutions for this issue is essential for ensuring your website's content gets properly indexed and ranked.
A sitemap is a file that provides search engines with information about the pages, videos, and other files on your site, and the relationships between them. It helps search engines crawl your site more intelligently and efficiently. Google's Search Console allows you to submit your sitemap and monitor its status, including any errors encountered during processing.
The message "Sitemap could not be read" appears when Google cannot retrieve or parse your sitemap file. This can hinder your site's indexing and affect your visibility in search results.
One of the most frequent issues is that the URL you provided for the sitemap is incorrect or has typos. Ensure that the URL is accessible and points directly to the sitemap file, typically located at a predictable path such as https://yourdomain.com/sitemap.xml.
If your server is experiencing downtime, the sitemap file might be temporarily unavailable. Check that the sitemap URL returns a 200 OK status code when accessed through a browser or a tool like cURL or an HTTP status checker.
Google expects sitemaps to adhere to XML sitemap protocols. Any syntax errors, invalid tags, or malformed XML can prevent proper reading of the file. Use online XML validators to verify the correctness of your sitemap.
Configuring your server to disallow bots or implementing security measures such as robots.txt files, IP whitelisting, or authentication can block Googlebot from accessing your sitemap. Ensure that your server permits access to the sitemap URL for Googlebot.
Large sitemaps exceeding 50,000 URLs or 50MB in size may cause issues. In such cases, breaking the sitemap into smaller files and using a sitemap index file is recommended.
Ensure the URL entered in Search Console matches the location of your sitemap file. Confirm there are no typos, and the URL is accessible from the web.
Open the sitemap URL in a browser. If the page loads correctly and displays valid XML code, it is accessible. If not, investigate the server or sitemap file issues.
Use online XML validation tools to ensure the sitemap is well-formed. Correct any errors identified and re-upload the sanitized sitemap file.
Review your server configuration to ensure no restrictions prevent Googlebot from fetching the sitemap. Update robots.txt to allow crawling of the sitemap URL, for example:
If your sitemap is large, consider splitting it into multiple smaller sitemaps and creating a sitemap index file that references all of them. This approach improves load times and reduces the chance of errors.
After ensuring the sitemap is correct and accessible, go to your Google Search Console account and remove the previous error entry, then resubmit the sitemap URL. This often prompts Google to re-crawl the sitemap and update its status.
Several online tools and resources can help diagnose and fix sitemap issues:
Maintaining a healthy sitemap is critical for optimal search engine indexing. Regular checks and adherence to SEO best practices will minimize errors and improve your website's visibility.
In the realm of e-commerce, particularly when using Shopify as a platform, sitemaps play a crucial role in ensuring that search engines can efficiently crawl and index the website's pages. A sitemap is essentially a file that provides search engines with a roadmap of your site's structure, including URLs, hierarchy, and update frequency.
However, Shopify store owners sometimes encounter issues such as "Shopify sitemap could not be read," which can impede search engine optimization (SEO) efforts. Understanding the causes and solutions for this problem is vital for maintaining optimal online visibility.
A Shopify sitemap is a dynamically generated XML file accessible at a standard location, typically yourdomain.com/sitemap.xml. This file lists all the significant pages, products, collections, blog posts, and other relevant content on your Shopify store.
Search engines use this sitemap to discover and understand the structure of your site, prioritizing crawling accordingly. Shopify creates and updates this sitemap automatically, ensuring that new content is reflected promptly.
If your server experiences downtime or slow response times, search engines may fail to access your sitemap. Shopify’s hosting infrastructure generally manages this well, but during maintenance or outages, the sitemap may temporarily be unreachable.
Sometimes, the sitemap URL is incorrect or changed inadvertently. Also, misconfigured robots.txt files or crawling restrictions can prevent search engines from accessing the sitemap.
At times, Shopify itself may experience technical issues or updates that temporarily affect URL accessibility. These are often resolved quickly by Shopify’s technical teams.
Local cache or browser issues can also give the illusion that the sitemap is not accessible or readable when in reality, the problem lies on the client side.
To diagnose this problem, you can perform the following checks:
Ensure that the URL is correct and matches the standard location provided by Shopify. The typical URL is https://yourdomain.com/sitemap.xml. Visit this URL directly to check if the sitemap loads properly.
Confirm that your site is accessible without errors. Use website monitoring tools to detect downtime, and ensure your Shopify store is operational.
Access your robots.txt file, usually at yourdomain.com/robots.txt. Ensure it does not contain directives blocking search engines from crawling the sitemap or important pages.
If you’re experiencing local caching issues, clear your browser cache and try accessing the sitemap again. Also, consider clearing any CDN caches if applicable.
If the issue persists, consult Shopify’s support team or visit their status page to see if there are ongoing platform issues affecting sitemap accessibility.
Managing your Shopify sitemap effectively can enhance your SEO efforts. Here are some tools and practices to keep in mind:
Shopify generates the sitemap.xml file automatically, reflecting any changes to products, collections, or pages. This automation reduces manual errors but also means that any underlying platform issues can temporarily affect sitemap availability. Staying informed about Shopify updates and platform status ensures that you can react promptly when issues arise.
Encountering a "Shopify sitemap could not be read" message can be concerning, but understanding the potential causes and proper troubleshooting steps can resolve the issue efficiently. Regular monitoring, verifying URL accessibility, and maintaining proper configurations help ensure that your store’s sitemap remains available for search engines, ultimately supporting your SEO strategy.
When managing a website, especially for SEO purposes, sitemaps are crucial for ensuring that search engines can effectively crawl and index your content. However, encountering errors such as "sitemap could not be read" or "couldn't fetch" can hinder this process and create confusion among website administrators. This article provides a comprehensive overview of these common sitemap errors, their causes, and practical solutions to resolve them.
A sitemap is a file that lists all the pages on a website, providing search engines with a clear structure of the site's content. It is typically written in XML format and helps search engines discover new or updated pages efficiently. Without an accurate sitemap, search engines might miss important pages, negatively impacting the site's SEO performance.
Errors related to sitemaps often appear when search engines attempt to read or fetch the sitemap file. Two of the most frequently reported issues are:
Understanding these errors requires delving into their possible causes, which can range from server issues to configuration mistakes.
If the URL of the sitemap is incorrect or has been changed, search engines will fail to locate or access the file. Common mistakes include typos, case sensitivity errors, or wrong directory paths.
Server downtime, firewall restrictions, or misconfigured server settings can prevent search engines from retrieving the sitemap file. If the server hosting the sitemap is temporarily unavailable or blocks certain user agents, fetch attempts will fail.
Incorrect permissions set on the sitemap file can restrict access, making it unreadable to search engine bots. Ensuring the file has proper read permissions is essential.
A malformed XML file or syntax errors within the sitemap can cause fetching issues. Validating the sitemap against XML standards helps identify such problems.
HTTP status codes like 404 (Not Found) or 500 (Server Error), or improper redirects can hinder access to the sitemap. Search engines may also struggle if the sitemap URL redirects to an incorrect or empty page.
Check the URL provided in your webmaster tools or robots.txt file. Confirm that it points to the correct location and that the URL is accessible via a web browser.
Use online tools or fetch the sitemap URL directly in a browser to see if it loads correctly. If it doesn't, identify whether the issue is due to server errors or network problems.
Ensure the sitemap file has appropriate permissions—generally, readable by everyone (e.g., 644). Also, check your server logs for any errors during fetch attempts.
Use XML validation tools to verify the sitemap's syntax. Correct any errors or inconsistencies and re-upload the file.
Make sure your server responds with a 200 status code for the sitemap URL, and avoid unnecessary redirects. If redirects are necessary, ensure they are properly configured to lead to the correct sitemap location.
Most search engines offer webmaster tools that help diagnose sitemap problems. In Google Search Console, for example, you can see detailed error reports for your submitted sitemaps. If you encounter the "couldn't fetch" error or similar messages, use the tools to identify specific issues such as server errors, URL problems, or format errors.
Address the highlighted issues based on the recommendations provided by these tools, and re-submit the corrected sitemap for indexing.
Maintaining a healthy and accessible sitemap is fundamental for effective website SEO. Regular monitoring, proper configuration, and adherence to best practices can prevent errors like "sitemap could not be read" or "couldn't fetch." When problems do occur, systematic troubleshooting helps identify and resolve issues swiftly, ensuring that search engines can crawl and index your content without hindrance.
Webmasters and SEO professionals often encounter the message "sitemap could not be read" when submitting or verifying sitemaps with Google Search Console. This message indicates that Googlebot was unable to access or parse the sitemap file correctly. Sitemaps are essential for informing search engines about the structure of a website, ensuring proper indexing and visibility. When this error appears, it can hinder your site's SEO performance and indexing efficiency.
Several issues can lead to the "sitemap could not be read" message. Identifying the root cause is crucial to resolving the problem effectively. The typical causes include:
Ensure that the URL you submitted is correct and accessible directly through a browser. Copy and paste it into the address bar to verify it loads without errors.
Use sitemap validation tools or XML validators to check for syntax errors. Properly formatted sitemaps should validate without issues.
Use online tools or developer consoles to perform a HTTP request to the sitemap URL. Confirm that the server returns a status code of 200 OK and the correct content type.
Check the robots.txt file to ensure it does not disallow the sitemap URL. A disallow rule can prevent Google from reading your sitemap.
Look into server logs to identify any errors or blocked requests. Ensure that security solutions or firewalls are not preventing Googlebot from accessing the sitemap.
Update the sitemap submission with the correct and accessible URL. Use absolute URLs and ensure there are no typos.
Run your sitemap through XML validators and correct any syntax issues. Ensure compliance with sitemap protocol standards.
Optimize server performance and uptime. Use reliable hosting providers and implement measures to prevent downtime.
Remove any disallow directives that block the sitemap URL. Whitelist Googlebot if necessary through security configurations.
Configure your server to serve the sitemap with the correct content type, typically application/xml.
Several online tools can assist in diagnosing and fixing sitemap issues:
Google periodically revisits sitemaps to re-index content. This process depends on the correctness and accessibility of the sitemap file. When Google cannot read your sitemap, it may skip indexing some or all URLs listed, potentially reducing your site's visibility. Ensuring consistent accessibility and correctness is vital for maintaining search engine visibility.
If troubleshooting does not resolve the issue, consider the following steps:
In many cases, persistent issues stem from misconfigurations or server problems that require a detailed review of hosting and URL management practices.
Maintaining a properly configured sitemap is integral to your website’s SEO health. Regular validation, prompt fixes for errors, and monitoring through Google Search Console help ensure your site’s content is correctly indexed and visible to the audience. Remember, an accessible and correctly formatted sitemap improves your site's chances of being fully understood and ranked by search engines.
When managing a website, ensuring that search engines can accurately crawl and index your content is essential for visibility. Google Search Console is a valuable tool that helps webmasters monitor and maintain their site's presence in Google search results. However, users occasionally encounter a common error message: "sitemap could not be read". This article provides a comprehensive overview of this issue, its causes, and practical solutions to help you resolve it effectively.
The message "sitemap could not be read" indicates that Google Search Console was unable to access, retrieve, or parse the sitemap file submitted for your website. A sitemap is an XML file that lists your web pages, helping search engines understand the structure of your site. When this error appears, it suggests that there is a problem with how the sitemap is hosted, formatted, or accessible, preventing Google from extracting the necessary information to enhance your site's visibility.
Start by testing the sitemap URL directly in a browser or using online tools. Verify that the file loads correctly without errors. Confirm that it matches the URL submitted in Google Search Console.
Use online XML validators or sitemap validation tools to ensure your file follows proper XML standards. Correct any syntax errors or structural issues identified.
If your server is unreliable or frequently experiences downtime, consider upgrading your hosting plan or switching to a more stable provider. This ensures consistent accessibility for search engines.
Ensure your web server serves the sitemap with the correct MIME type (application/xml). Consult your hosting provider or server documentation for instructions on setting this up correctly.
Your robots.txt file should permit Googlebot to fetch the sitemap URL. An overly restrictive robots.txt file may prevent access, leading to read errors.
Google periodically updates its crawling and indexing protocols. Staying informed helps you adjust your site management practices accordingly.
Encountering the "sitemap could not be read" error is common but manageable with systematic troubleshooting. The key is to verify the url, ensure proper formatting, confirm server accessibility, and follow best practices for sitemap management. By addressing these areas, you improve your site's visibility and ensure search engines can efficiently crawl your content.
Many Shopify store owners encounter the error message "sitemap could not be read" when attempting to access or submit their website's sitemap. This issue can prevent search engines from properly indexing your site, thereby impacting your SEO efforts. Understanding the causes, troubleshooting steps, and solutions can help you resolve this problem efficiently.
A sitemap is a file that provides search engines with information about the pages, videos, and other files on your website. It helps search engines crawl your site more intelligently and efficiently. For Shopify merchants, having a well-structured sitemap ensures that your products, categories, and other content are discoverable and properly indexed.
Typically, Shopify generates a sitemap automatically, which is accessible through a URL like https://yourstore.com/sitemap.xml. Search engines use this sitemap to understand your site’s structure, prioritize content, and improve search visibility. When the sitemap cannot be read, this crucial process is interrupted, which can negatively impact your SEO performance.
One common reason why this error appears is that the sitemap URL is not accessible or is entered incorrectly. Shopify automatically generates the sitemap, but sometimes URL misconfiguration or typos may lead to failed access attempts.
Sometimes, server-side issues, such as CDN disruptions or network connectivity problems, can prevent your sitemap from being read by search engines or tools. These issues are often temporary and resolve without further intervention.
The robots.txt file controls what content search engines can index. If it contains restrictive directives or blocks access to the sitemap URL, search engines may be unable to read the sitemap file.
If the sitemap file has incorrect formatting, invalid XML, or corruption, search engines might fail to parse it properly, resulting in the "could not be read" message.
Third-party apps or custom theme modifications can sometimes interfere with the automatic sitemap, either by altering the file or blocking access, leading to read errors.
Ensure that you are accessing the correct URL, typically https://yourstore.com/sitemap.xml. Double-check for typos or incorrect subdomains. You can also try visiting the URL in different browsers or devices to confirm accessibility.
Test your site's accessibility using online tools to identify if there are server-side issues. Clear your browser cache and attempt to access the sitemap again. If there's a widespread connectivity problem, waiting for hosting services to resolve the issue is advised.
Inspect your robots.txt file to ensure it does not block access to /sitemap.xml. The file should contain no Disallow directives related to the sitemap. If you find restrictions, modify or remove them to allow search engines to access the sitemap.
Use online XML validators or sitemap validation tools to ensure the sitemap file adheres to XML standards. Correct any errors or inconsistencies that may prevent parsing.
If you suspect third-party apps or custom code modifications interfere with your sitemap, temporarily disable them and check if the problem persists. Revert to default Shopify settings if needed.
Shopify automatically creates a sitemap.xml file, accessible directly through the /sitemap.xml link. Ensure that this default file is available and not overridden or deleted through theme edits or app interventions.
Regularly verify the correctness and accessibility of your sitemap. Keep your site and themes updated to avoid compatibility issues. Use Google Search Console or similar tools to monitor how search engines crawl and index your site. Regular checks help identify and resolve issues proactively.
The "Sitemap could not be read" error prevents Google from properly crawling your website
When Google displays this error in Search Console, it means their crawlers failed to process your sitemap file. This critical issue prevents Google from discovering and indexing your pages, effectively making your content invisible in search results.
This problem is especially common for large websites with thousands or millions of URLs, where Google's crawl budget becomes exhausted before processing your entire sitemap.
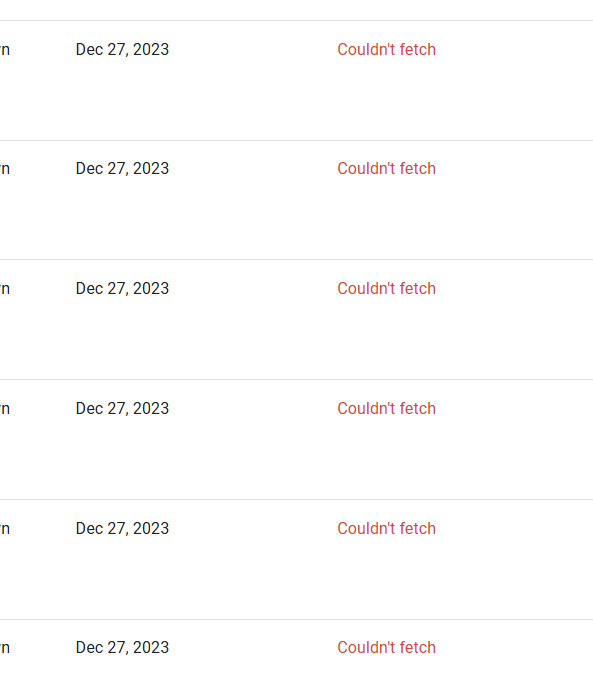
Understanding the root causes helps you find the right solution
Too many URLs for Google to process efficiently within their crawl limits
GoogleBot has quotas per site that can be quickly exhausted on large sites
Timeouts, slow responses, or server errors when Google tries to fetch your sitemap
Invalid XML structure, encoding issues, or exceeding the 50MB/50K URL limits
Save your time by avoiding these common dead ends
Google rarely provides direct support for individual sitemap issues, and responses can take weeks with no resolution.
Hours spent on Stack Overflow, Reddit, and SEO forums yield outdated advice that rarely addresses the core problem.
Unlike temporary crawl errors, this issue persists indefinitely without intervention.
Many indexing services make promises but lack the technology to actually solve crawl budget limitations.
IndexJump uses advanced technology to ensure your pages get indexed
A simple four-step process to get your pages indexed
Add your sitemap URL to IndexJump's dashboard
Our system processes your URLs efficiently
Pages get discovered and indexed by Google
Track your indexing progress in real-time
Real results from real website owners
"After months of struggling with sitemap errors, IndexJump fixed everything in days. Our traffic increased by 40%."
"We have over 2 million pages. No other service could handle it. IndexJump did."
"The free trial convinced me. I could see GoogleBot hitting our pages in real-time."
Everything you need to know about fixing sitemap errors
This error occurs when Google's crawlers cannot properly read or process your sitemap file. Common causes include large website size exceeding crawl budget, server timeouts during sitemap fetching, XML formatting issues, or the sitemap exceeding Google's 50MB/50,000 URL limits.
Google prioritizes crawl resources across billions of websites. Individual site issues, especially for non-enterprise sites, don't receive dedicated support. Their automated systems have fixed budgets per domain, and there's no manual override available through standard support channels.
IndexJump uses advanced technology to ensure your URLs are properly discovered and indexed by Google, bypassing the limitations of traditional sitemap submission. Our system strategically presents your URLs to Google's crawlers in a way that maximizes indexing success.
Yes! IndexJump offers a free trial for up to 100 URLs. This allows you to verify that the technology works by checking your server logs for GoogleBot visits. No credit card is required to start the trial.
Most users see GoogleBot activity in their server logs within 24-48 hours. Full indexing typically occurs within 1-2 weeks, depending on the number of URLs and your site's existing authority. You can monitor progress in real-time through the IndexJump dashboard.
Start with a free trial - no credit card required